Encryption Techniques
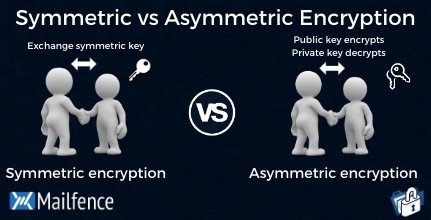
Symmetric and asymmetric encryption are the two types of encryptions used. The name of the phrase depends on whether the same key is used for encryption and decryption.
Asymmetric Encryption
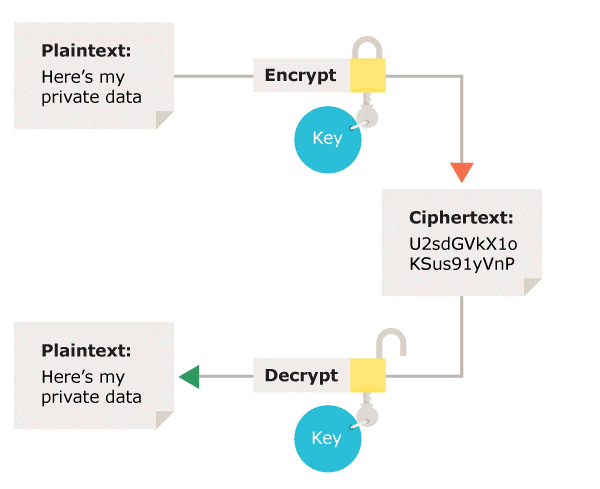
The same key is used for encryption and decryption in symmetric encryption. Therefore, it is crucial to take into account a secure way while transferring the key between the sender and recipient.
Symmetric Encryption
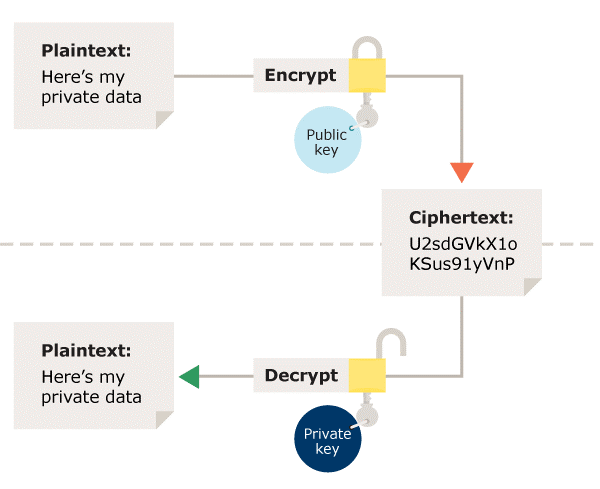
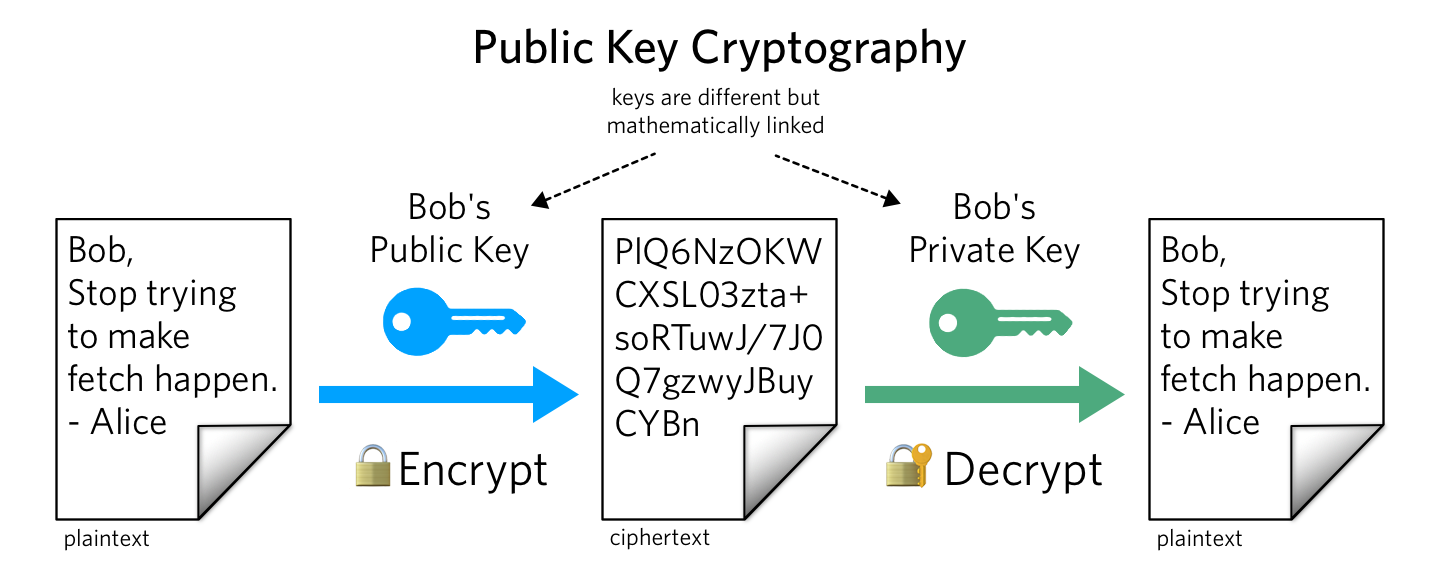
A key pair is used in asymmetric encryption; a distinct key is used for encryption and decryption. Typically, one of the keys is referred to as the private key, and the other as the public key. The owner keeps the private key a secret, while the authorised recipients or the general public have access to the public key.
Only the appropriate private key can be used to decrypt data that has been encrypted using the recipient's public key. As a result, data transfers can be made without worrying about unauthorised or illegal access.
Public key
A public key is what the sender uses to encrypt their message. For example, if you were to send a letter, you would place it in a post box. The post box's encryption would prohibit anyone from accessing the mail, just as it would be impossible for anyone to read an encrypted message.
A private key is what the recipient uses to decrypt the message. For instance, the private key would be the key the postman would use to open the post box, granting access to the letter that was protected by the post box. This would be an example of the recipient decrypting the message so they can read the decrypted information.
Businesses and organisations are accountable for any customer's data that they collect after joining the organisation or business. In order to ensure that the firm is keeping the data secure, rules and policies must be adhered to. However, data breaches may also be very costly and harm a company's reputation if their data was compromised, leading their target market to view them as unprofessional and lose all faith in the compromised organisation.
Hashing
A technique called hashing creates a fixed-length value that summarises the contents of a file or message. It's frequently mischaracterized as an encryption technique. Hash functions are employed with cryptography to offer digital signatures and integrity checks, but because no secret key is utilised, the hash cannot be used to re-create the message, the message is not made private.